Compounds with hydrogen bonds exist either in the liquid or gaseous state. Second it occurs between a hydrogen atom of one molecule and a very small and electronegative atom.

Hydrogen Bond Definition Types And Examples
The atom that loses an electron becomes a positive ion.

. Types of H- Bonds. It is maximum in the solid state and minimum in the gaseous state. The most stable arrangement is the.
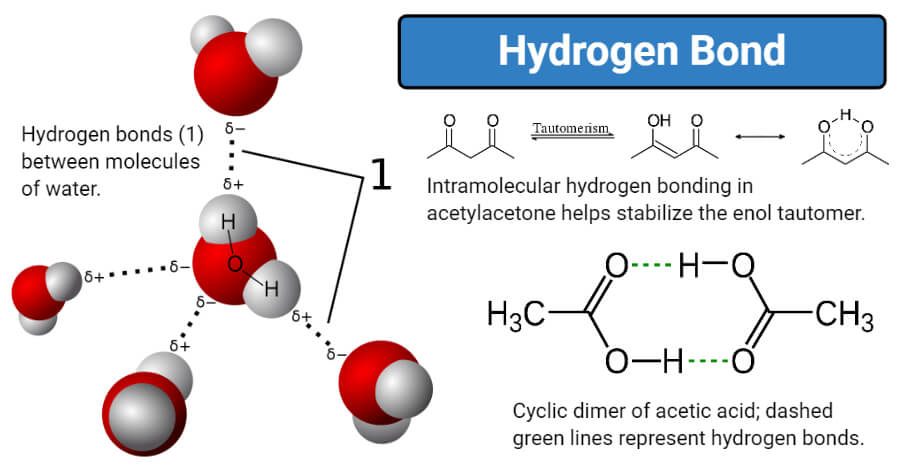
Matter is made up of molecules and and atoms. The physical force of attraction which holds atoms and molecules in a matter is called physical bond. Many organic carboxylic acids form hydrogen-bonded dimers in the solid state.
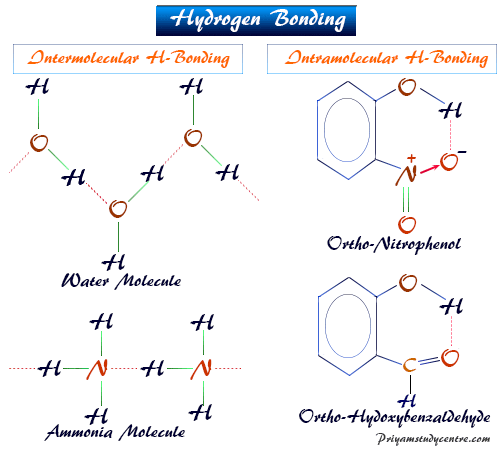
It is capable of extensive hydrogen bonding with water molecules. There is more to it. Based on the type of interactions the hydrogen bond is classified into two types they are intermolecular hydrogen bonding and intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
The physical state of a compound determines the strength of a hydrogen bond. Describe the differences of inter and intra molecular forces. At 25 o C nitrosyl fluoride ONF is a gas whereas water is a liquid.
The structural formula of dimethyl ether. London dispersion forces not responsible for the difference between these two compounds. The bond which is made due to the behaviour of atom to become stable is called chemical bond.
Compounds with stronger bonds exist in the liquid state whereas those with weaker hydrogen bonds exist in the gaseous state. Sugar sucrose is soluble in water despite being a covalent molecule. Hydrogen bonding is responsible for ammonia s remarkably high solubility in water.
The magnitude of hydrogen bonding depends on the physical state of the compound. All of the electron pairsshared and unsharedrepel each other. Explain why the halogens exist in different physical states at room temp in terms of this intermolecular force.
First a hydrogen bond is an attractionforcebond between two molecules. Thus the hydrogen bonds have a strong influence on the structure and properties of the compounds. Hydrogen bonds can be seen between molecules.
ONF and water have about the same shape. In covalent bonding electrons are shared between two atoms but in hydrogen bonding this kind of sharing doesnt take place. The relatively large electronegativity difference between oxygen and hydrogen about 23 is the reason why the partially positively charged try to think why they are partially positively charged hydrogens are attracted to the lone pairs on the oxygen atoms of other water molecules.
Here the hydrogen bonding acceptor is the electron cloud of a benzene ring. Relationship between intermolecular forces and melting point boiling point and physical state. The electronic configuration of hydrogen is 1s 1The nucleus of hydrogen is surrounded by only one electron in 1s orbital with the maximum capacity of two electrons.
Covalent bonds are stronger than hydrogen bonds. The ions in ionic solids are close to each other so ionic attractions are strong. Thus hydrogen bonding arises from water molecules due to the dipole-dipole interaction between the hydrogen atom of a water molecule and the oxygen atom of another H2O molecule.
Therefore hydrogen has the capability for forming a single covalent chemical bond but if the covalently. And there are a lot of ionic compounds which are insoluble in water of course. Aldehydes and ketones cannot form a hydrogen bond with themselves but can hydrogen bond with water molecules.
As the size of the molecules increase so do the dispersion forces the attraction. Physical Consequences of Hydrogen Bonding. A hydrogen bond tends to be stronger than van der Waals forces.
Hydrogen atom should be there to have a hydrogen bond. There are exceptions to this of course. Here the location of bond electrons in the O-H bond is very close to the oxygen nucleus due to.
This is because the oxygen atom in addition to forming bonds with the hydrogen atoms also carries two pairs of unshared electrons. It is mainly two types intramolecular and intermolecular Hydrogen bonds. A water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded to an oxygen atom and its overall structure is bent.
The atom that gains an electron becomes a negative ion. Vander waals forces coulombic forces are physical forces. There are two types of hydrogen bonds.
Hydrogen bonds are important in. The electrostatic attraction between these ions is an ionic bond. As the intermolecular forces increase from top to bottom in Table 49 the melting and boiling points increase.
Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers electrons to another atom. Types of hydrogen bonding. Ammonia mp 78 bp 33C is hydrogen-bonded in the liquid and solid states.
The reason is hydrogen bonding. One of the slightly positive hydrogen atoms in a water molecule is attracted to one of the lone pairs on the oxygen atom of an aldehyde or. A hydrogen bond is a dipole-dipole force and is an attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen on one molecule and a slightly negative atom on another molecule.
The strength of the bond depends on the electronegativity of the atom bound to hydrogen. Bond means force of attraction. Which can form a hydrogen bond and which has only dispersion.
ONF has a higher molecular weight 49 amu than water 18 amu. Covalent bonds can be occurred between any two atoms. This bond always involves a hydrogen atom.
Hydrogen bonds can occur between molecules or within parts of a single molecule. For example in water molecules H2O hydrogen is bound together by an electronegative oxygen atom. A hydrogen bond is a type of attractive dipole-dipole interaction between an electronegative atom and a hydrogen atom bonded to another electronegative atom.
The physical properties of aldehydes and ketones are explained below. Solubility of a solid in water without reaction suggests it is ionic. Hydrogen bonding is very strong in the solid state but minimal in the gaseous state.
Hydrogen Bond Definition Properties Types Formation Examples

How Is Hydrogen Bonding Among Water Molecules Related To The Structure Of The Water Molecule Socratic Water Molecule Chemistry Education Teaching Chemistry

What S Up With That The Mysterious Effect That Makes Hot Water Freeze Faster Than Cold Hydrogen Bond Chemistry Lessons Water Molecule
0 Comments